Eajack LeetCode Notes- Day5
PS:偷懒原因,很多题目不再看best solution了…… :)
收获:以后刷题一看题,先想最简单暴力求解,先不管时间复杂度、空间复杂度等要求,保证首次AC。之后,再优化大O。稳中求优!不然时间浪费太多了!
Q28
(1) 题目信息
- 标题:验证回文串
- 编号&难度:[125],easy
- Tags:
two-pointers|string- 描述:给定一个字符串,验证它是否是回文串,只考虑字母和数字字符,可以忽略字母的大小写。说明:本题中,我们将空字符串定义为有效的回文串。
- 例子:
输入: "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama" 输出: true 输入: "race a car" 输出: false
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=125 lang=cpp
*
* [125] 验证回文串
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
//1- 清洗s
string s_clear = "";
for(int i=0; i<s.size(); i++)
{
if((s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'z') || \
(s[i] >= 'A' && s[i] <= 'Z') || \
(s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'))
s_clear += s[i];
}
//2- 重新遍历s_clear
if(s_clear.size() == 0 || s_clear.size() == 1)
{
return true;
}
int head = 0, tail = s_clear.size()-1;
while(head < tail)
{
if( s_clear[head] == s_clear[tail] || \
( (isalpha(s_clear[head]) && isalpha(s_clear[tail])) && \
(abs(s_clear[head]-s_clear[tail]) == abs('A'-'a')) ) )
{
head++; tail--;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
- 思路:首先清洗字符串s,只保留:字母&数字。之后,对清洗后string首尾部双指针检测
Q29
(1) 题目信息
- 标题:只出现一次的数字
- 编号&难度:[136],easy
- Tags:
hash-table|bit-manipulation- 描述:给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。说明:你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?
- 例子:
输入: [2,2,1] 输出: 1 输入: [4,1,2,1,2] 输出: 4
(2) 个人Code
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> num_times;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++)
{
if(num_times.find(nums[i]) != num_times.end())
{
num_times.erase(nums[i]);
}
else
{
num_times[nums[i]] = 1;
}
}
return (num_times.begin())->first;
}
};
- 思路:hash表典型题目。遍历nums,进行hash;若当前num在hash表find到了,证明num出现了2次,则删掉key = num的item。最后,hash表仅剩出现1次的num,return即可。
Q30
(1) 题目信息
- 标题:环形链表
- 编号&难度:[141],easy
- Tags:
linked-list|two-pointers- 描述:给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数
pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果pos是-1,则在该链表中没有环。- 进阶:你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
- 例子:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。 输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。 输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:false 解释:链表中没有环。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=141 lang=cpp
*
* [141] 环形链表
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_map<ListNode*,int> nodeMap;
ListNode* temp = head;
while(temp != NULL)
{
if(nodeMap.find(temp) != nodeMap.end())
{
return true;
}
nodeMap[temp] = 1;
temp = temp->next;
}
return false;
}
};
- 思路:hashmap记录节点,遍历链表,若当前节点出现过,则return true。
Q31
(1) 题目信息
- 标题:最小栈
- 编号&难度:[155],easy
- Tags:
stack|design- 描述:设计一个支持 push,pop,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
- push(x) — 将元素 x 推入栈中。
- pop() — 删除栈顶的元素。
- top() — 获取栈顶元素。
- getMin() — 检索栈中的最小元素。
- 进阶:你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
- 例子:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack(); minStack.push(-2); minStack.push(0); minStack.push(-3); minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3. minStack.pop(); minStack.top(); --> 返回 0. minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=155 lang=cpp
*
* [155] 最小栈
*/
//https://blog.csdn.net/alps1992/article/details/41741811
class MinStack {
public:
vector<long> stack;
long stackMin = 0;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
if(stack.empty())
{
stack.push_back(0);
stackMin = x;
}
else
{
stack.push_back(x-stackMin);
stackMin = (x<stackMin)?(x):(stackMin);
}
}
void pop() {
if(stack.back() < 0)
{
stackMin -= stack.back();
stack.pop_back();
}
else
{
stack.pop_back();
}
}
int top() {
return (stack.back() < 0)?(stackMin):(stack.back()+stackMin);
}
int getMin() {
return stackMin;
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(x);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->getMin();
*/
- 思路:其实这里是看了:https://blog.csdn.net/alps1992/article/details/41741811的思路。最小栈,会额外保留最小值stackMin;push是储存(x-stackMin),同时stackMin更新;pop是若stackMin < 0,更新stackMin -= stack.back(),stack.pop_back();top,return (stack.back() < 0)?(stackMin):(stack.back()+stackMin)
Q32
(1) 题目信息
标题:相交链表
编号&难度:[160],easy
Tags:
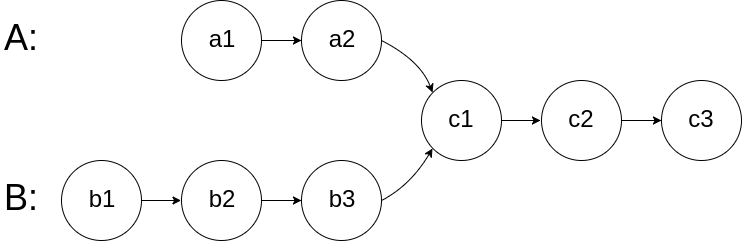
linked-list描述:编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
例子:
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
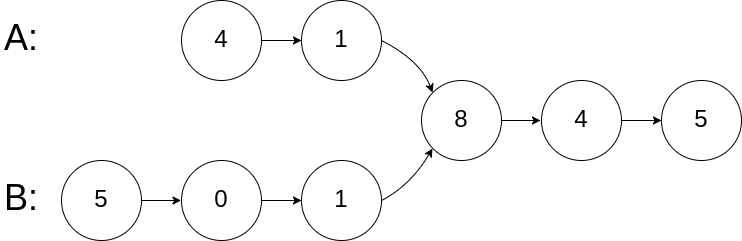
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Reference of the node with value = 8 输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。示例 2:
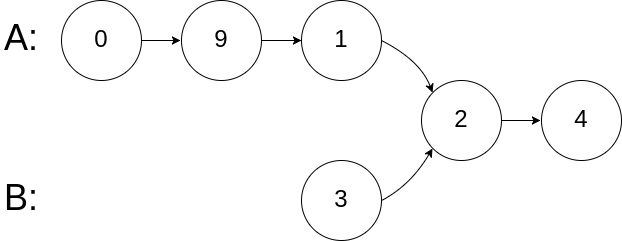
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Reference of the node with value = 2 输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。示例 3:
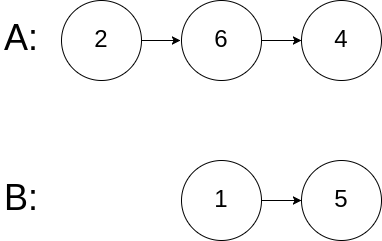
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回
null.- 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=160 lang=cpp
*
* [160] 相交链表
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(headA == headB && headA == nullptr) return headA;
//1- O(n^2)
/* ListNode* tempA = headA;
while(tempA != nullptr)
{
ListNode* tempB = headB;
while(tempB != nullptr)
{
if(tempA == tempB)
{
return tempA;
}
tempB = tempB->next;
}
tempA = tempA->next;
}
return nullptr;*/
//2- O(n)
unordered_map<ListNode*, int> nodeMap;
ListNode *tempA = headA, *tempB = headB;
while(tempA != nullptr)
{
nodeMap[tempA] = 1;
tempA = tempA->next;
}
while(tempB != nullptr)
{
if(nodeMap.find(tempB) != nodeMap.end())
{
return tempB;
}
tempB = tempB->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
- 思路:2种思路O(n^2) & O(n)。O(n^2),遍历List1,对当前Node1和List2所有Node比较,若地址相等,则return true,最后return false。O(n),引入hashmap首先储存所有List1节点地址,再遍历List2,map.find是否有Node,2次O(n),即为O(n)。
Q33
(1) 题目信息
编号&难度:[167],easy
Tags:
array|two-pointers|binary-search描述:给定一个已按照升序排列 的有序数组,找到两个数使得它们相加之和等于目标数。
函数应该返回这两个下标值 index1 和 index2,其中 index1 必须小于 index2。
说明:
- 返回的下标值(index1 和 index2)不是从零开始的。
- 你可以假设每个输入只对应唯一的答案,而且你不可以重复使用相同的元素。
例子:
输入: numbers = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9 输出: [1,2] 解释: 2 与 7 之和等于目标数 9 。因此 index1 = 1, index2 = 2 。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=167 lang=cpp
*
* [167] 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& numbers, int target) {
int i = 0, j = numbers.size()-1;
while(i < j)
{
if(numbers[i]+numbers[j] == target)
{
return {i+1,j+1};
}
else if(numbers[i]+numbers[j] > target)
{
j--;
}
else if(numbers[i]+numbers[j] < target)
{
i++;
}
}
return {0,0};
}
};
- 思路:注意升序=>二分查询,首尾部2指针查询,判断(numbers[i]+numbers[j] == target),大于则尾部指针递减,小于则首部指针递增
Q34
(1) 题目信息
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=168 lang=cpp
*
* [168] Excel表列名称
*/
class Solution {
public:
string convertToTitle(int n) {
string res="";
while(n>0){
res=char('A'+(n-1)%26)+res;
n=(n-1)/26;
}
return res;
}
};
思路:纯数学题。。。看了solution的,本质就是二进制形式幂函数:
28 = 26 + 2 = 26^1 * 1 + 26^0 * 2 = 26^1 * 'A' + 26^0 * 'B' = "AB"
Q35
(1) 题目信息
编号&难度:[167],easy
Tags:
array|two-pointers|binary-search描述:给定一个已按照升序排列 的有序数组,找到两个数使得它们相加之和等于目标数。
函数应该返回这两个下标值 index1 和 index2,其中 index1 必须小于 index2。
说明:
- 返回的下标值(index1 和 index2)不是从零开始的。
- 你可以假设每个输入只对应唯一的答案,而且你不可以重复使用相同的元素。
例子:
输入: numbers = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9 输出: [1,2] 解释: 2 与 7 之和等于目标数 9 。因此 index1 = 1, index2 = 2 。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=167 lang=cpp
*
* [167] 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& numbers, int target) {
int i = 0, j = numbers.size()-1;
while(i < j)
{
if(numbers[i]+numbers[j] == target)
{
return {i+1,j+1};
}
else if(numbers[i]+numbers[j] > target)
{
j--;
}
else if(numbers[i]+numbers[j] < target)
{
i++;
}
}
return {0,0};
}
};
- 思路:注意升序=>二分查询,首尾部2指针查询,判断(numbers[i]+numbers[j] == target),大于则尾部指针递减,小于则首部指针递增
Q36
(1) 题目信息
标题:求众数
编号&难度:[169],easy
Tags:
array|divide-and-conquer|bit-manipulation描述:给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的众数。众数是指在数组中出现次数大于
⌊ n/2 ⌋的元素。你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在众数。例子:
输入: [3,2,3] 输出: 3 输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2] 输出: 2
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=169 lang=cpp
*
* [169] 求众数
*/
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> numsTimes;
for(auto num: nums)
{
//注意:numsTimes[num]初始化为0
if(++numsTimes[num] > nums.size()/2)
return num;
}
return -1;//trash code
}
};
- 思路:简单,又可以用hashmap的。遍历nums,添加num入hashmap作为key,同时判断当前(++numsTimes[num] > nums.size()/2)return num。(因为题干说一定有众数),return -1属于trash code。
Q37
(1) 题目信息
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=171 lang=cpp
*
* [171] Excel表列序号
*/
class Solution {
public:
int titleToNumber(string s) {
if(s=="") return 0;
long s_num = (s.back()-'A'+1), cnt = 1;
for(int i=s.size()-2; i>=0; i--)
{
s_num += ((pow(26,cnt)) * (s[i]-'A'+1));
cnt++;
}
return s_num;
}
};
- 思路:Q34逆问题。关键:
28 = 26 + 2 = 26^1 * 1 + 26^0 * 2 = 26^1 * 'A' + 26^0 * 'B' = "AB"
Q38
(1) 题目信息
标题:旋转数组
编号&难度:[189],easy
Tags:
array描述:给定一个数组,将数组中的元素向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
例子:
输入: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] 和 k = 3 输出: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4] 解释: 向右旋转 1 步: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6] 向右旋转 2 步: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5] 向右旋转 3 步: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4] 输入: [-1,-100,3,99] 和 k = 2 输出: [3,99,-1,-100] 解释: 向右旋转 1 步: [99,-1,-100,3] 向右旋转 2 步: [3,99,-1,-100] 说明: 尽可能想出更多的解决方案,至少有三种不同的方法可以解决这个问题。 要求使用空间复杂度为 O(1) 的 原地 算法。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=189 lang=cpp
*
* [189] 旋转数组
*/
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
//源代码:左右比较,暴力
/* int right_i = k%nums.size(), left_i = nums.size()-left_i;
if(right_i <= left_i)
{
while(right_i--)
{
int lastNum = nums.back();
for(int j=nums.size()-1; j>0; j--)
{
nums[j] = nums[j-1];
}
nums[0] = lastNum;
}
}
else
{
while(left_i--)
{
int firstNum = nums[0];
for(int j=0; j<nums.size()-1; j++)
{
nums[j] = nums[j+1];
}
nums[nums.size()-1] = firstNum;
}
}*/
//solution,绝妙
// 这个方法基于这个事实:当我们旋转数组 k 次,
// k%n个尾部元素会被移动到头部,剩下的元素会被向后移动。
if(k%nums.size())
{
reverse(nums.begin(),nums.end());//反转整个数组
reverse(nums.begin(),nums.begin()+k%nums.size());//反转前k个元素
reverse(nums.begin()+k%nums.size(),nums.end());//反转后面n-k元素
}
}
};
- 思路:方法1:暴力k%nums.size()次(因为nums.size()次后数组不变),ac报错,因为有个很复杂输入导致超时;方法2:巧妙至极……(solution做法)
Q39
(1) 题目信息
标题:颠倒二进制位
编号&难度:[190],easy
Tags:
bit-manipulation描述:颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。
例子:
输入: 00000010100101000001111010011100 输出: 00111001011110000010100101000000 解释: 输入的二进制串 00000010100101000001111010011100 表示无符号整数 43261596, 因此返回 964176192,其二进制表示形式为 00111001011110000010100101000000。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=190 lang=cpp
*
* [190] 颠倒二进制位
*/
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
bitset<32> bin_num(n);
string bin_n_str = bin_num.to_string();
uint32_t n_reverse;
int head = 0, tail = bin_num.size()-1;
while(head < tail)
{
char digit = bin_n_str[head];
bin_n_str[head] = bin_n_str[tail];
bin_n_str[tail] = digit;
head++; tail--;
}
bitset<32> bin_reverse(bin_n_str);
if(bin_reverse.size() != 0)
{
n_reverse = bin_reverse.to_ulong();
return n_reverse;
}
return 0;
}
};
- 思路:没啥说的,关键标准库class:bitset<32> bin_num(n),百度可知,用于十进制 <=> 二进制,无技巧,solution 太技巧了,不喜欢。
Q40
(1) 题目信息
标题:位1的个数
编号&难度:[191],easy
Tags:
bit-manipulation描述:编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数,返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数(也被称为汉明重量)。
例子:
输入:00000000000000000000000000001011 输出:3 解释:输入的二进制串 00000000000000000000000000001011 中,共有三位为 '1'。 输入:11111111111111111111111111111101 输出:31 解释:输入的二进制串 11111111111111111111111111111101 中,共有 31 位为 '1'。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=191 lang=cpp
*
* [191] 位1的个数
*/
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int one_cnt = 0;
while(n > 0)
{
if(n & 1) one_cnt++;
n >>= 1;
}
return one_cnt;
}
};
- 思路:简单,先和1相与,后右移,直到n <= 0。
Q41
(1) 题目信息
标题:移除链表元素
编号&难度:[203],easy
Tags:
linked-list描述:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
例子:
输入: 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6 输出: 1->2->3->4->5
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=203 lang=cpp
*
* [203] 移除链表元素
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
//clear val in the front
while(head && head->val == val)
{
head = head->next;
}
//begin clear
ListNode *nowNode = head, *previousNode=nullptr;
while(nowNode)
{
if(nowNode->val == val)
{
ListNode* temp = nowNode;
nowNode = nowNode->next;
previousNode->next = nowNode;
delete temp;
}
else
{
//update nodes
previousNode = nowNode;
nowNode = nowNode->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
- 思路:首先删除首部为val值节点,然后线性遍历删除val节点。关键在于第一步 & delete的链表操作。
Q41
(1) 题目信息
标题:计数质数
编号&难度:[204],easy
Tags:
hash-table|math描述:统计所有小于非负整数 n 的质数的数量。
例子:
输入: 10 输出: 4 解释: 小于 10 的质数一共有 4 个, 它们是 2, 3, 5, 7 。
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=204 lang=cpp
*
* [204] 计数质数
*/
class Solution {
public:
int isPrime(int n)
{
for(int i=2; i*i<=n; i++)
{
if(n%i == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
int countPrimes(int n) {
if(n<3) return 0;
int prime_cnt = 1;
for(int i=3; i<n; i++)
{
if(isPrime(i))
prime_cnt++;
}
return prime_cnt;
}
};
- 思路:简单。内置isPrime函数判断是否为质数,遍历n,逐个判断,计数。
Q42
(1) 题目信息
标题:反转链表
编号&难度:[206],easy
Tags:
linked-list描述:反转一个单链表。
例子:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=206 lang=cpp
*
* [206] 反转链表
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//1- O(N)空间复杂度
/* ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
vector<ListNode*> nodes;
//push
while(head != nullptr)
{
nodes.push_back(head);
head = head->next;
}
//pop
ListNode* head_reverse = nodes.back();
ListNode* nowNode = head_reverse;
nodes.pop_back();
for(int i=nodes.size()-1; i>=0; i--)
{
ListNode* temp = nodes[i];
nowNode->next = temp;
nowNode = nowNode->next;
}
nowNode->next = nullptr;
return head_reverse;
}*/
//2- O(1) 空间复杂度,迭代
/* ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){
if(!head || !(head->next)) return head;
ListNode *head_reverse = head->next, *previousNode = head, \
*temp = nullptr;
head->next = nullptr;
while(head_reverse->next != nullptr)
{
temp = head_reverse->next;
head_reverse->next = previousNode;
previousNode = head_reverse;
head_reverse = temp;
}
head_reverse->next = previousNode;
return head_reverse;
}*/
//3- O(1) 空间复杂度,递归
ListNode* reverseList_sub(ListNode* previousNode, ListNode* nowNode){
if(nowNode->next)
{
ListNode* head_reverse = reverseList_sub(nowNode, nowNode->next);
nowNode->next = previousNode;
return head_reverse;
}
else
{
nowNode->next = previousNode;
ListNode* head_reverse = nowNode;
return head_reverse;
}
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){
if(!head || !(head->next)) return head;
ListNode *nowNode = head->next;
head->next = nullptr;
ListNode* head_reverse = reverseList_sub(head, nowNode);
return head_reverse;
}
};
- 思路:典型题。3种解法:(1)- O(n)空间复杂度,栈push节点,栈pop节点;(2)- 迭代,O(1)原地操作;(3)- 递归,O(1)原地操作。
Q43
(1) 题目信息
标题:存在重复元素
编号&难度:[217],easy
Tags:
array|hash-table描述:给定一个整数数组,判断是否存在重复元素。如果任何值在数组中出现至少两次,函数返回 true。如果数组中每个元素都不相同,则返回 false。
例子:
输入: [1,2,3,1] 输出: true 输入: [1,2,3,4] 输出: false 输入: [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2] 输出: true
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=217 lang=cpp
*
* [217] 存在重复元素
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> numsMap;
for(auto num:nums)
{
if(numsMap.find(num) != numsMap.end())
{
return true;
}
else
{
numsMap[num] = 1;
}
}
return false;
}
};
- 思路:hashmap典型题。2次重复变种,这里可以多次重复。
Q44
(1) 题目信息
标题:存在重复元素 II
编号&难度:[219],easy
Tags:
array|hash-table描述:给定一个整数数组和一个整数 k,判断数组中是否存在两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] = nums [j],并且 i 和 j 的差的绝对值最大为 k。
例子:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3 输出: true 输入: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1 输出: true 输入: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1 输出: true
(2) 个人Code
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=219 lang=cpp
*
* [219] 存在重复元素 II
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool containsNearbyDuplicate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int,vector<int>> numsMap;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++)
{
if(numsMap.find(nums[i]) != numsMap.end())
{
numsMap[nums[i]].push_back(i);
}
else
{
numsMap[nums[i]] = {i};
}
}
//遍历numsMap
for(auto it=numsMap.begin(); it!=numsMap.end(); it++)
{
vector<int> m_2 = it->second;
if(m_2.size() >= 2)
{
for(int i=0; i<m_2.size(); i++)
{
for(int j=i+1; j<m_2.size(); j++)
{
if(abs(m_2[i]-m_2[j]) <= k)
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
- 思路:上题变种。先存下来,再遍历map。